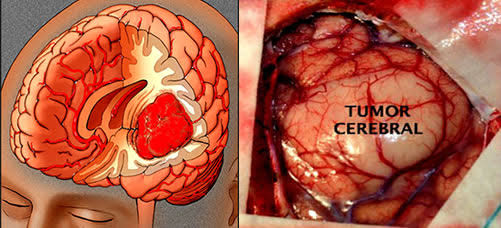
WHAT IS A BRAIN TUMOR?
A primary brain tumor is a mass or an abnormal cell growth, arising from in brain cells or the structures around it.
Secondary brain tumor or metastasis refers to cancer that begins elsewhere in the body spreads, reaching the brain, where it forms a tumor.
There are different types of brain tumors, depending what cells it develops from.
The two most common types are:
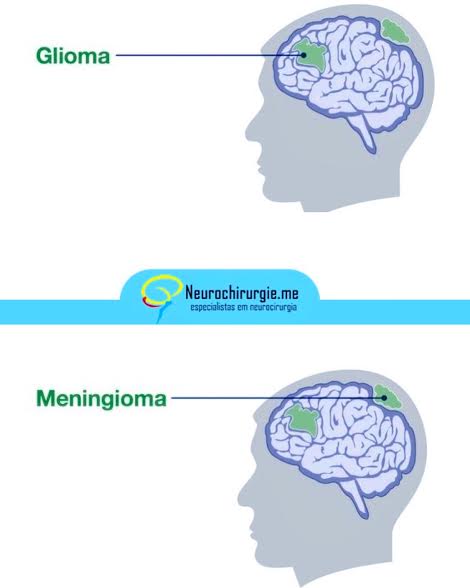
GLIOMA: type of tumor that occurs in the brain and spinal cord. They begin in the gluey supportive cells (glial cells) that surround nerve cells. The symptoms of glioma vary by tumor’s location, and it can compromise brain functions. Beware: gliomas do not arise from neurons!
MENINGIOMA: tumor that grows from the meninges (protective membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord). They are usually benign (not cancer) and are more often found in middle-aged women. Symptoms first appear as headaches and seizures, caused by increased pressure of the growing tumor. They are located “outside” the brain.
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF A BRAIN TUMOR?
Symptoms depend on the size, location and growth of the tumor.
Both an intra-axial (inside the brain) and extra-axial tumor (around the brain, but inside the skull) may compromise the brain functions and present with:
✔ Frequent progressive headaches that do not improve with the use of analgesics;
✔ Nausea and vomiting;
✔ Blurred vision or visual loss (it is important to note that this is NOT a refraction disorder – when the problem is corrected by wearing glasses);
✔ Slurred speech (as in a stroke);
✔ Dizziness and vertigo;
✔ Hearing loss;
✔ Mental confusion (advanced stages of progressive growth and larger tumors).
WHAT IS THE TREATMENT FOR A BRAIN TUMOR?
✔ NEUROSURGERY:
Has the objective of removing the tumor without causing neurological damage (several options are used to guide the surgeon without affecting functional brain areas, such as functional resonance, Neuronavigator, stereotaxis, intraoperative monitoring, awake craniotomy, etc). When total resection is not possible, in order not to damage important areas of the brain, adjuvant therapy is required (e.g. radiotherapy)
The tissue from the removed tumor material is sent to the laboratory for analysis (biopsy) to make the diagnosis and determine the complementary therapy.
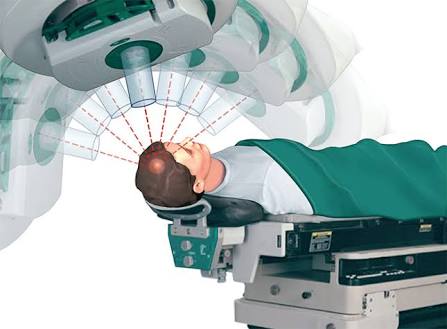
✔ RADIATION THERAPY:
Uses high-energy beams to destroy or inhibit the growth of abnormal cells that form the tumor (x-rays, gamma rays or protons).
It is used in different situations: after surgery, to destroy cancer cells that hat may remain after surgery; as the main treatment (when surgery is not possible) or to relieve the symptoms of the disease.
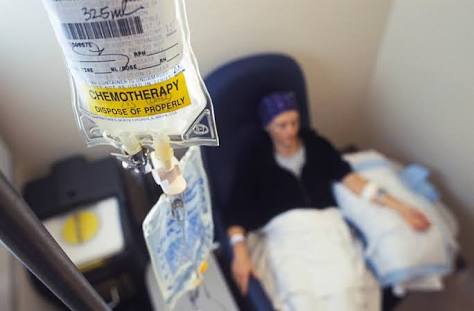
✔ CHEMOTHERAPY:
Uses drugs to kill cancer cells. As it is a systemic treatment, it also affects the body’s healthy cells (the reason why there are so many side effects).
It is used in conjunction with surgery or radiation therapy to help in the treatment of malignant brain tumors. It can be used separately in cases of tumors in advanced stages, with the chances of a cure are decreased.
QUAIS OS SINTOMAS DE UM TUMOR CEREBRAL?
Sintomas dependem do tamanho, localização e taxa de crescimento.
Tanto um tumor intra-axial (dentro do cérebro) como extra-axial (ao redor do cérebro, mas dentro do crânio) podem comprometer as funções cerebrais e se apresentar com:
✔️ Dor de cabeça progressiva e que não melhora com analgésicos, frequentemente.
✔️Náuseas e vômitos;
✔️Visão borrada ou perda de campo visual (ressalte que NÃO é um distúrbio da refração – quando o problema se corrige com uso de óculos);
✔️Fala arrastada (Como em um AVC);
✔️Tontura e vertigem;
✔️Perda auditiva;
✔️Confusão mental (estágios avançados, quando de crescimento progressivo e de grande tamanho).





QUAL O TRATAMENTO DE UM TUMOR CEREBRAL?
- ✔️NEUROCIRURGIA:
Objetivo de remover o tumor sem causar dano neurológico (opções diversas são utilizadas para guiar o cirurgião sem afetar áreas cerebrais funcionais, como Ressonância funcional, Neuronavegador, estereotaxia, monitorização intra-operatória, craniotomia com paciente acordado etc). Quando não é possível a ressecção total, afim de não lesionar áreas nobres do cérebro, terapia adjuvante é necessária (radioterapia, p.ex.)
O material do tumor retirado é utilizado para estabelecer o diagnóstico (biópsia) e guiar a terapia complementar.
- ✔️RADIOTERAPIA:
Feixes de alta energia ionizante são utilizados para destruir ou inibir o crescimento das células anormais que formam o tumor (raios x, raios gama ou prótons).
É aplicada em diferentes situações: após a cirurgia para destruir as células cancerígenas que sobraram da cirurgia; como tratamento principal (quando não é possível operar) ou para aliviar sintomas da doença.
- ✔️QUIMIOTERAPIA:
Usa drogas que matam as células tumorais. Por ser um tratamento sistêmico, atinge também as células sadias do organismo (por isso tanto efeitos colaterais são vistos).
É utilizada junto com a cirurgia ou radioterapia para auxiliar no tratamento dos tumores malignos cerebrais. Pode ser utilizada isoladamente naqueles tumores em estágios avançados, sem possibilidade de cura.