TBI results from a violent blow to the head, and possible forms of TBI are:
INTRACRANIAL HEMATOMA: is a collection of blood within the skull. There are different categories of hematoma: EPIDURAL HEMATOMA – occurs when a blood vessel, usually an artery, ruptures between the outer surface of the dura mater (outer membrane of the brain) and the skull.
SUBDURAL HEMATOMA – occurs when blood vessels rupture, causing blood accumulation Blood accumulations between the brain and the outermost of three membrane layers that cover your brain (dura mater)
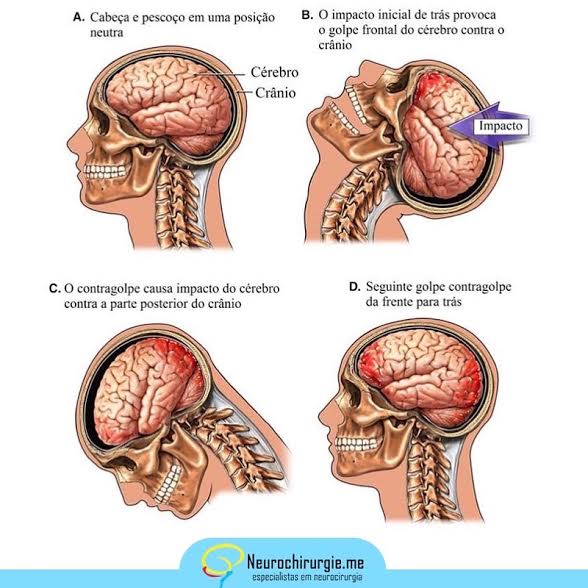
HEMORRHAGIC CONTUSION – brain injury that causes bleeding and swelling around of the area where the trauma occurred (coup and contrecoup is one of its patterns – figure 2).
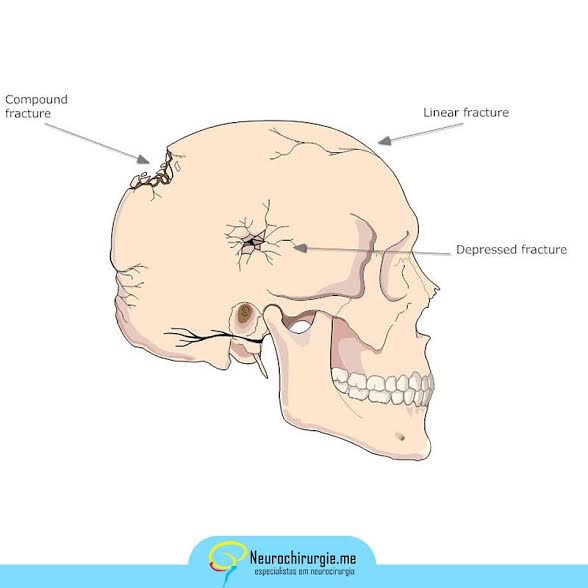
SKULL FRACTURES: different types of skull fracture are closed, open (when the skin is broken and the bone emerges; can cause infections), linear or depressed (in this case, a fracture may cause the skull to indent or extend into the brain cavity) (figure 1).
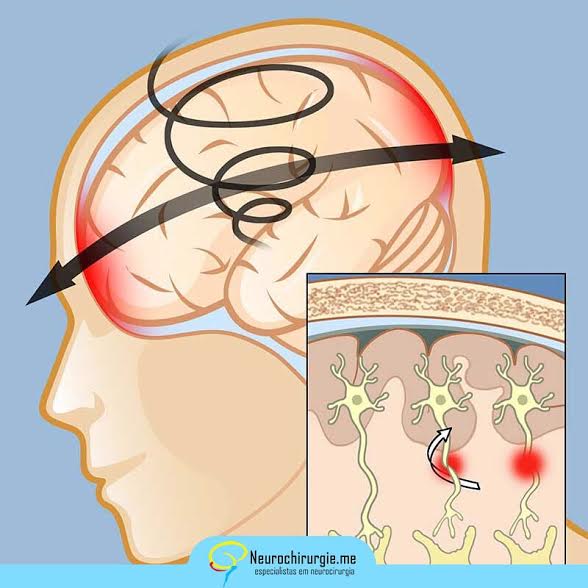
DIFFUSED AXONAL INJURY: Caused by a rapid acceleration or sudden deceleration movement, not necessarily involving head collision. This injury causes the disruption of nerve fibers (axons of neurons) (Figure 3). Patients may remain in a coma for a long period, with no evident changes in skull imaging tests.